Continuous Strip Footing Drawing Cea Commerial Foundations Cea
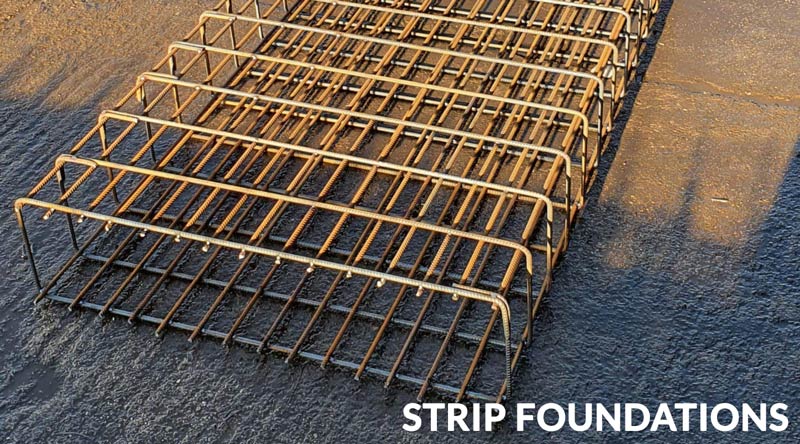

Sometimes referred to as a strip footing, a strip foundation is a type of shallow foundation often used within low to medium rise residential buildings. Suitable only where the ground conditions are stable and with good load-bearing capacity, strip foundations are fast and cost-effective to build.
When Are Strip Foundations Suitable?
Generally speaking, foundations are classed as either deep foundations or shallow foundations, and the choice of what type of foundation to use on any construction project is dependent on a number of factors, including the building itself, ground conditions, access, budgets and timeframes.

Strip foundations are just one of several types of shallow foundation. They can be used to support load-bearing walls, where the load-bearing capacity of the underlying ground has been evaluated and is deemed to be sufficient for the project. Strip foundations can also be used to support closely-grouped columns.
Careful evaluation of the ground conditions across the whole footprint of the building is vital, in order to establish the overall load-bearing capacity of the plot, any weaker areas, and any other factors, such as access restrictions, water flows or other conditions that might impact the foundations. As an example, in areas of the site where the load-bearing capacity of the ground is reduced, a wider strip footing may be required, and the concrete should also be reinforced with appropriate steel reinforcement products.
As previously mentioned, strip foundations are only suitable for low to medium rise buildings where the underlying ground conditions are very good. They are typically only used for domestic residential projects, including new-builds and extensions. For sites where the ground conditions are unfavourable, or for high-rise or substantially-sized buildings, deep foundations are required, and strip foundations should never be used (Cons, 2020).

Looking for Steel Reinforcement?
We stock everything you need for concrete reinforcement; from loose cut and bent rebar, to prefabricated cages, mesh, and all the accessories you'll need to do the job right.
The Benefits of Strip Foundations
Where they can be used appropriately, strip foundations offer significant advantages. They are relatively inexpensive in terms of construction and materials, and they are well-understood by both construction professionals and manual labour personnel. Construction of strip foundations is quick and straightforward, with only the simplest of formwork structures and reinforcement installation required.
The Limitations of Strip Foundations
As we've discussed, strip foundations are only suitable for fairly small construction projects, with a relatively low loading requirement. Where soil conditions are weak or irregular, using strip foundations could have very serious consequences, potentially leading to structural integrity issues or even collapse. Strip foundations may also be unsuitable on sloping sites, or sites where a retaining wall is required.
A Step-By-Step Guide To Using Strip Foundations
- Identify and mark out the location of all load-bearing walls
- Excavate trenches, using each wall's centre line as a guide
- If required, dig the trenches deeper than necessary and backfill with compacted hardcore
- Construct formwork to support the poured concrete
- Position steel reinforcement, either rods or mesh panels, as appropriate, and tie in with suitable ties and stays
- Pour concrete into the trenchwork, ensuring level, even coverage and consistency
- Leave the concrete to set for the recommended length of time, before removing the formwork.
- Excavated spoil can be used to backfill the space where the formwork has been removed.
Strip foundations are only suitable for projects where the load-bearing capacity of the ground is adequate. As soil types may include gravel, sand, clay and silt, each with their own unique properties, bearing capacities and weaknesses, it is essential to carry out a geotechnical survey of the entire site before starting a construction project. A Standard Penetration Test (SPT) may be carried out to identify the soil type and composition, and the results of this test should be fed into the design process to ensure that the most suitable type of foundation is selected for the project. The relevant standards for foundation depth and width should also be referenced and adhered to, as part of the overall design stage. Recommended strip footing widths are shown in the diagram below: (Engineers, 2022)

Strip footing design example
Here's a rough guide to calculating the minimum width for a given structure weight (qallowable)
qultimate is the maximum weight of the structure multiplied by the safety factor.
Given data:
Unit weight of soil γ = 19.5KN/m³
Cohesive strength of soil c = 10KN/m²
Angle of internal friction Φ = 20°
Water table depth = Below influence zone
Footing depth Df = 1m
qallowable = 125KN/m
Factor of safety FOS = 3
Strip Footing width B = ?
Equations:
qultimate = Sc×c×Nc + q×Nq + 0.5×Sγ×γ×B×Nγ
qultimate = qallowable ×FOS = 125KN/m × 3 = 375KN/m
q = Df × γ = 1 × 19.5KN/m³ = 19.5KN/m³
Terzaghi's Bearing capacity equation: qu =C/Nc + γ Df Nq + 0.5 γ B N γ
Solution:

From the above table
At Φ = 20°, Nc = 17.5, Nq = 7.4, Nγ = 5.0
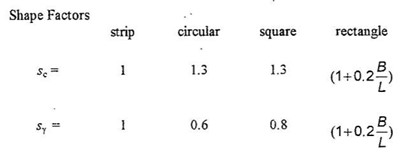
For strip footing, from the above table
Sc = 1, Sγ = 1
Putting all values in above equation
375 = 1×17.5×10 + 19.5×7.4 + 0.5×1×19.5×5×B
B = 1.14m
PLEASE NOTE: This is an example equation added purely to demonstrate the given equations and concepts. This calculation should not be used for anything other than the example here. Any and all calculations you require should be carried out by registered, experienced engineers and only after local soil testing and load bearing requirements have been established. As such, we will not be responsible for any failures or damages caused by using these results.
Source: https://www.reinforcementproductsonline.co.uk/news/strip-foundations/
0 Response to "Continuous Strip Footing Drawing Cea Commerial Foundations Cea"
Post a Comment